How to choose diamonds correctly?
1. Carat
The commonly heard scores of 30 and 50 refer to diamonds weighing 0.3ct and 0.5ct.

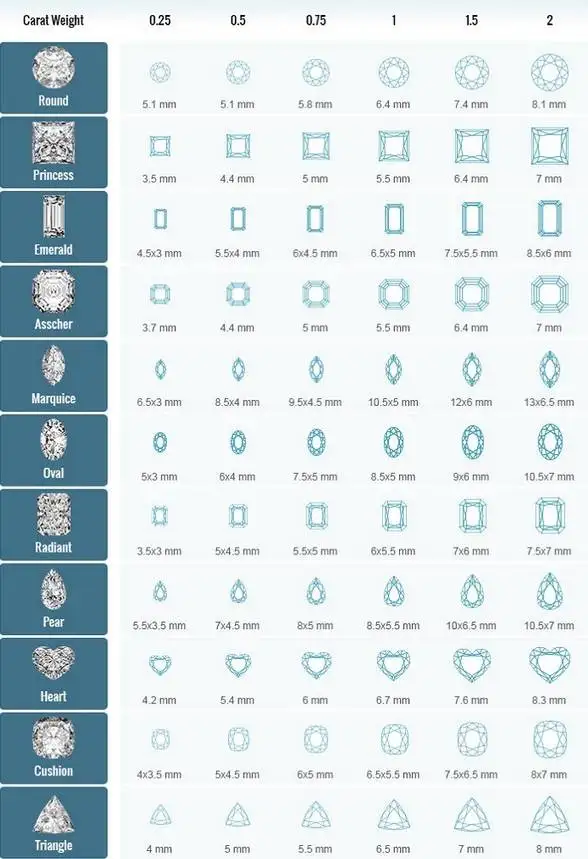
Diamonds of the same weight will exhibit different sizes on the countertop due to different cuts.
To be honest, under the same weight, a square will visually be about 15% larger than a circle.
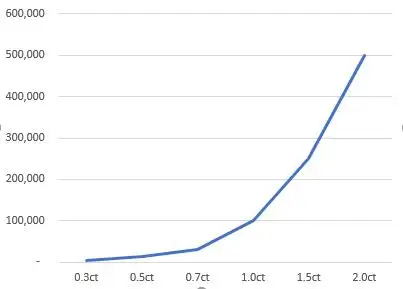
Everyone knows that the larger a diamond, the higher its price. However, the price and weight of a diamond do not increase proportionally, but With a whoosh Grow in a geometric progression.
Tip:
Diamonds weighing over 1 carat have collectible value, while diamonds weighing over 0.3ct have room for preservation.
2、Color
Diamond color grading is the grading of diamonds into different levels based on their degree of yellowing. D level is the highest and Z level is the lowest. Those below Z are generally used as industrial drills, also known as diamonds.
The color deviation of a white diamond can affect its value. Taking the yellow tone as an example, the more yellow the diamond is, the lower its value.
However, if the color is severely yellow and reaches a certain saturation, it can be called a yellow diamond. It belongs to the category of colored diamonds, and the more yellow, the better.
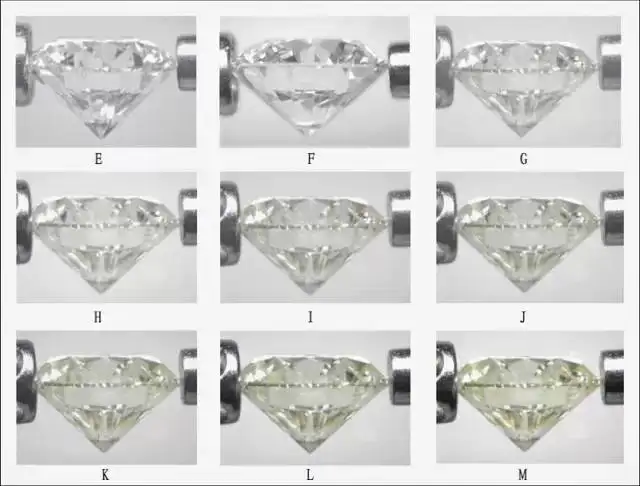

Tip:
1. As both colorless grades, the price of F color will be lower than that of D color in the same grade, which is more cost-effective.
2. Although the diamond matching stones used in inlay are small, using high white diamonds can also make the finished product more white and shiny than ordinary white diamonds.
3、Clarity
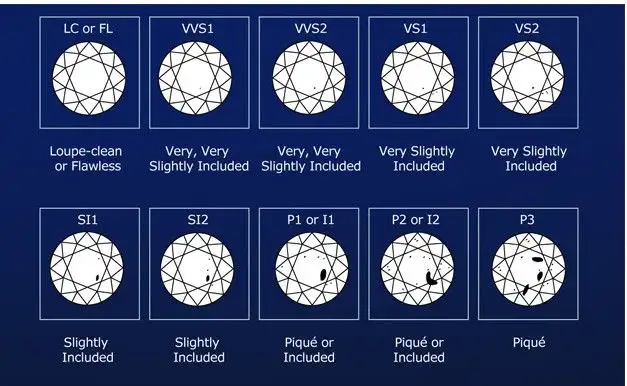
Clarity refers to the relative degree of diamond clarity characteristics observed by trained diamond grading personnel with normal vision under an artificial standard light source with a color temperature of 5500-6500, using an achromatic, equal optical path ten times magnifying glass.
Diamonds often contain needle like, cloud like, feather like cracks, and other colored minerals. The contents can affect the refraction of light, easily blocking or deflecting the light, and also affect the color tone of the diamond.
Tip :
1. Actually, the contents above the Sl1 level are difficult to observe with the naked eye and do not constitute visual defects. When choosing diamonds with a purity of SI1 or above, you can avoid overly demanding cleanliness and allocate more budget to other parameters.
2. How can SI2 and P1 be distinguished? It's very simple, it's at a distance of 30 centimeters to the naked eye. If defects can be seen, it's a P-grade diamond, and if defects cannot be seen, it's a SI2 grade diamond.
4、Cut
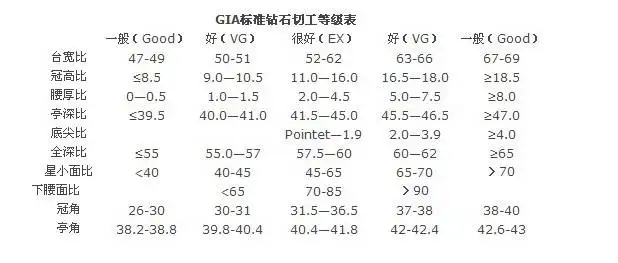
Cutting directly affects the brilliance of diamonds, and the ideal cutting is to make the diamond reflect almost all the light entering the diamond, making it appear vibrant and vibrant.
Cutting grading can be divided into Excellent, Very Good, Good, and Fair.
Less than 3% of diamond cutters can be called Excellent.
Although ideal cutting can bring us the most dazzling diamond, diamond dealers always need to balance the quality of cutting and weight loss, hoping that the cut diamond can bring the maximum profit. This is also why ideal cut diamonds are so rare.
5、Fluorescence
Diamonds emit a colored light such as blue or yellow light under strong ultraviolet radiation, which can be classified according to intensity levels:
There are five levels: NONE, FAINT, MEDIUM, Strong, VERY Strong.

Fluorescence reactions generally do not have a significant impact on the value of diamonds, except for diamonds with very strong fluorescence, which may appear oily and unclean under natural light, resulting in a discount in price.
If it is a colored diamond series, the situation is different. Fluorescence will enhance the color of colored diamonds, so if there is fluorescence of the same color as the body color, it is an added bonus.
6. Cutting shape
In addition to round diamonds, diamonds are often cut into different shapes. Under the same weight and quality, the price of diamonds cut differently also varies.
The shape of diamond stones is the fundamental reason why they are cut into different shapes. The shape into which a raw stone is cut has the lowest loss, and it is reasonable to choose which shape to cut.
However, due to the high market demand, many raw stones, even if cut into circular drills, will suffer greater losses and will still choose circular cutting.
Tips:
1. When the size and quality of diamonds are the same, the price of emerald cut diamonds is lower than that of round diamonds. You can buy larger rings under the same budget conditions.
2. Under the same weight, choosing a square cut diamond is more advantageous. The visual effect of diamonds cut by Princess Fang will be about 15% larger than that of round diamonds.
3. When wearing a pear shaped cut diamond ring, the fattest pear belly should be pushed towards the back of the hand, with the tip facing outward. Wearing it in this way will modify the shape of the hand. Under the premise of equal carats, pear shaped diamonds will appear larger than other cuts, making the wearer's fingers look very slender and attractive.
Frequently heard rumors:
7. Is' Eight Hearts and Eight Arrows' a Good Diamond?

In fact, the Eight Hearts and Eight Arrows are not special cutting techniques, but the pattern effect presented by ordinary round drills when their cutting level reaches a certain standard. Seeing eight hearts and eight arrows does not necessarily mean that diamonds have good cutting skills.
As long as the width ratio and depth ratio of the diamond are controlled within a reasonable range, eight arrows can be seen in the crown and eight hearts can be seen in the pavilion through a cutting mirror.
8. Is a diamond with a waist size good?
Merchants often express that our diamonds have a "waist size" and a very high-end appearance. What is this "waist size"? In fact, "waist code" refers to the GIA laser code of a diamond that has issued a GIA certificate. It is a GIA certificate number engraved on the diamond waist using laser technology. This laser code can be seen under a tenfold magnifying glass. For consumers who have just come into contact with diamonds, many people check the diamond and GIA certificate through the laser number on the diamond waist.
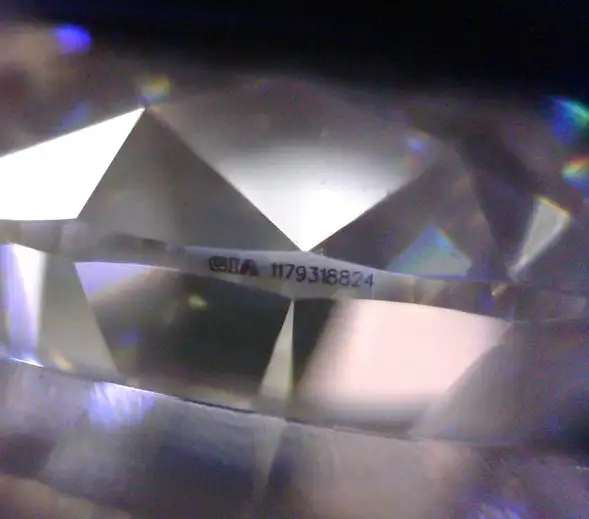

Not all GIA rated diamond waists are engraved with laser codes.
There are two types of diamond grading certificates issued by GIA:
a、GIA diamond dossier,
b、GIA diamond grading report
Due to the fact that the "small certificate" is a certificate issued for diamonds smaller than 1ct, and there is no "clarity sketch" of the diamond on the certificate, the GIA certificate code is engraved on the waist of the diamond to help customers identify the diamond. The three letters "GIA" are double line hollowed out.

And "Da Zheng" stipulates that there must be a "clarity sketch", generally without laser code. This is to maintain the perfection of the big diamond in all aspects as much as possible.

- Company Info
- Feedback
- Customer Reviews
- About Us
- Dropshipping
- FAQ
- User Center
- Forget Password
- My Orders
- Tracking Order
- My Account
- Register
- Payment & Shipping
- Terms And Conditions
- Return Policy
- Shipping Methods
- Payment Methods
- Discount
